Radiation safety is critical in various U.S. industries where employees face significant exposure risks. This blog delves into the top three high-risk sectors, emphasizing the need for stringent safety protocols to protect workers.
Understanding radiation risks in these environments is not just about compliance; it’s about safeguarding health and ensuring every worker returns home safely. We can appreciate the importance of continuous monitoring and proactive safety measures by exploring how these industries manage these risks.
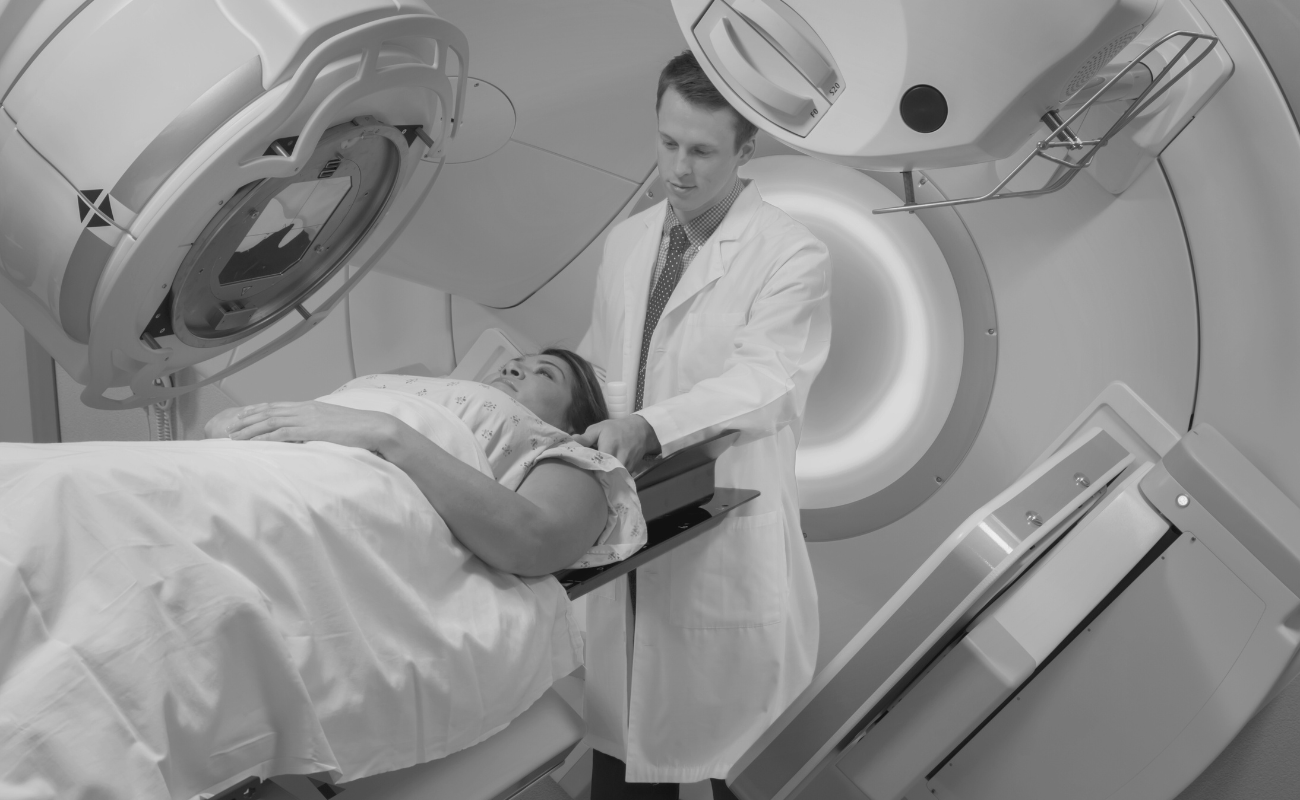
Healthcare industry’s radiation risks
In the healthcare industry, radiation safety is paramount due to the frequent use of radiological equipment for diagnostics and treatment, such as X-rays and CT scans. Workers, including radiologists and technicians, face exposure risks that can have long-term health effects.
Radiation safety protocols are crucial to minimize exposure and protect health. Measures such as lead-lined barriers, wearing protective lead aprons, and strict adherence to safety guidelines help ensure that the benefits of these medical imaging technologies are achieved without compromising the health and safety of those who operate them.
Regular training and monitoring are also vital to maintaining a safe environment, underscoring the ongoing commitment required in healthcare settings to uphold radiation safety standards.
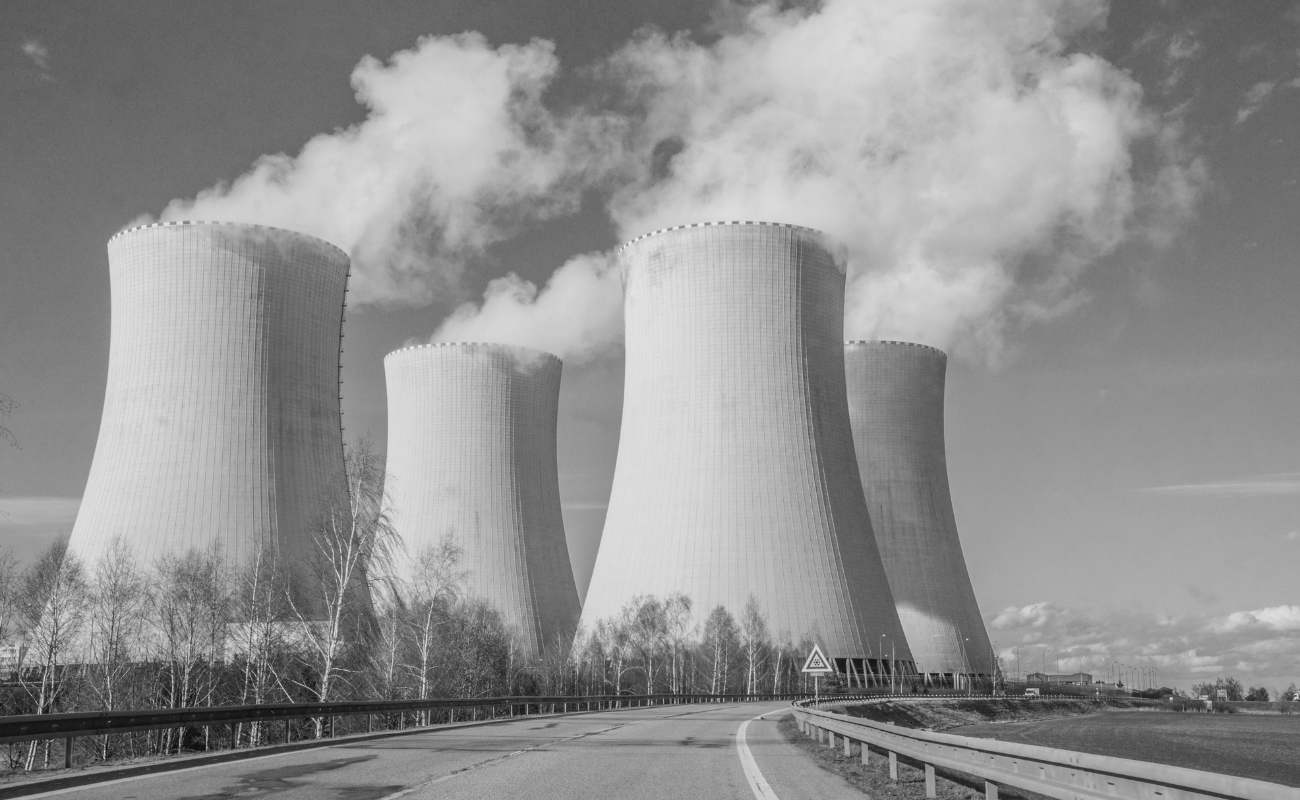
Nuclear sector exposure
Occupational hazards in nuclear power plants
Nuclear power plants are critical facilities that harness atomic energy but pose specific radiation risks to their workforce. Employees are potentially exposed to various types of radiation, such as alpha, beta, gamma rays, and neutrons, each originating from different parts of the nuclear reaction process.
For example, gamma rays, the most penetrating type of radiation, can emanate from reactor cores and spent fuel. Neutrons, released during nuclear fission, pose a significant risk due to their high energy and potential to induce other radioactive materials.
Strategies for minimizing risk in nuclear workplaces
Ensuring radiation safety in nuclear facilities involves a robust system of monitoring, containment, and emergency response protocols. Radiation monitoring systems are crucial, including personal dosimeters workers wear to measure exposure and large-scale detectors that monitor ambient radiation levels.
Containment methods are also vital; these include reinforced concrete structures that prevent radiation escape and systems designed to contain radioactive leaks. Moreover, comprehensive emergency procedures are established to respond to incidents involving evacuation plans, decontamination processes, and medical readiness to treat radiation exposure.
These measures are essential in upholding radiation safety standards, ensuring that nuclear energy’s benefits do not come at the cost of employee health and safety.

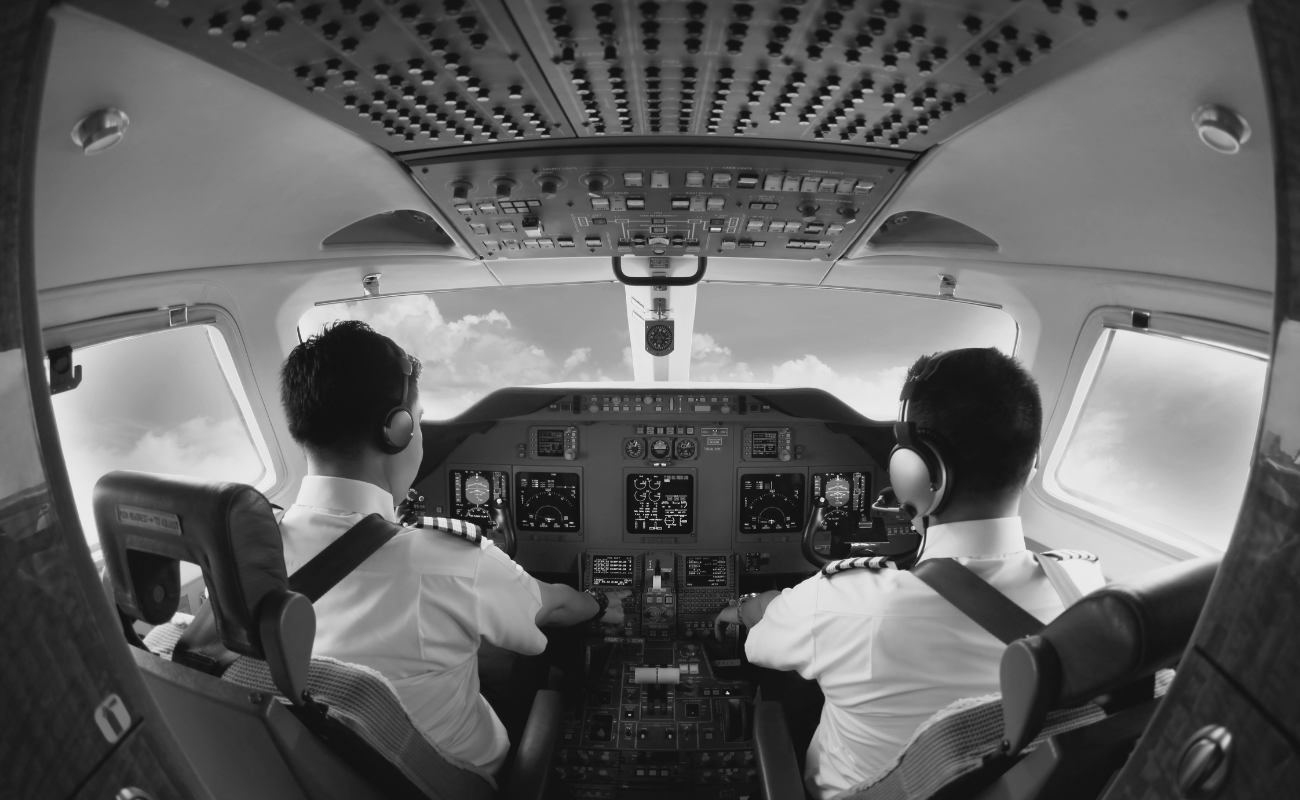
Aviation and aerospace radiation concerns
Cosmic radiation exposure for flight crews
Airline staff, especially flight crews, are exposed to higher levels of cosmic radiation due to the altitudes at which commercial aircraft operate. Cosmic radiation intensity increases with altitude because there is less atmospheric shielding. Furthermore, flight routes near the poles are subject to higher radiation levels due to the Earth’s magnetic field configuration, which allows more cosmic rays to penetrate. These factors mean that pilots and cabin crew are exposed to significantly more cosmic radiation than ground-based personnel.
Protective practices for aviation professionals
The aviation industry employs various technologies and training to mitigate the risks of cosmic radiation exposure. Modern aircraft have radiation detection instruments that help monitor exposure in real-time. Aviation professionals are also trained in scheduling practices that limit their exposure, such as managing flight routes and times to reduce time spent at high-risk altitudes and latitudes.
Additionally, regulatory bodies enforce strict limits on the amount of exposure permitted for aircrews, ensuring their health remains protected while performing their duties.
Learn more about our equipment to monitor radiation exposure.

Conclusion
As we conclude our exploration of radiation safety in three high-risk industries in the U.S., it’s clear that maintaining rigorous safety protocols is crucial. Across healthcare, nuclear power, and aviation sectors, dedicated efforts to manage radiation exposure safeguard workers’ health and ensure operational safety.
Implementing advanced monitoring systems, strict safety training, and adhering to regulatory standards are indispensable. By continuously enhancing these practices, we protect those at the forefront of these critical industries and contribute to a safer, healthier workplace environment. Understanding and mitigating radiation risks is not just a regulatory obligation—it’s a fundamental aspect of maintaining public and environmental health.
