
Ionizing radiation is a type of energy released through the spontaneous disintegration of unstable atoms, and can come from natural sources such as radioactive elements, as well as artificial sources like nuclear plants and medical procedures. This type of energy can have negative effects on human health, making it crucial to control and measure exposure to it using equipment that delivers the amount of radiation in Sievert or microSievert units. Our expert company offers a selection of radiation monitoring devices that can help ensure the safety of those working in radiation-prone environments.
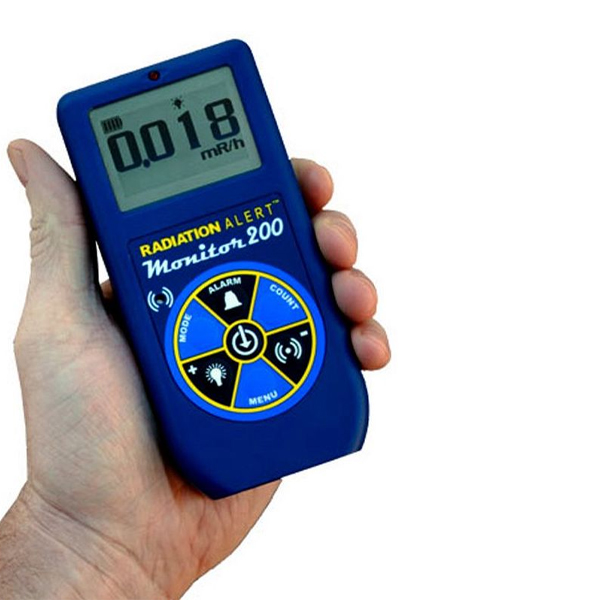

There are different types of radiation monitoring devices available, depending on the specific application and the type of radiation being measured. Some common types of radiation monitoring devices include personal radiation dosimeters, area radiation monitors, handheld radiation detectors, Geiger counters, and scintillation detectors. Each type of device has its own advantages and limitations, and the choice of device will depend on the specific requirements of the application.
Radiation monitoring devices work by detecting and measuring ionizing radiation. The specific method of detection depends on the type of device, but typically involves some type of radiation sensor that can detect and convert the energy from ionizing radiation into an electrical signal. The device then analyzes the signal to determine the amount and type of radiation present. Personal radiation dosimeters, for example, are often worn as badges and use a film or thermoluminescent detector to measure the radiation dose received by an individual. Area radiation monitors, on the other hand, are designed to monitor a specific area for radiation and may use a combination of sensors such as Geiger-Muller tubes, ion chambers, or scintillation detectors. Handheld radiation detectors are portable and can be used to detect radiation in various settings, while Geiger counters and scintillation detectors are more specialized devices that can detect different types of radiation such as alpha, beta, gamma or X-rays. Overall, radiation monitoring devices provide crucial information on radiation levels and help ensure safety in various settings.
There are several benefits to using radiation detectors in radiation-prone environments:
Overall, radiation detectors play a critical role in ensuring the safety of workers in radiation-prone environments, compliance with safety regulations, early detection of potential incidents, and providing peace of mind to those working in these environments.
Radiation monitoring and radiation detection are related but distinct concepts. Radiation detection refers to the process of detecting the presence of ionizing radiation using specialized equipment such as radiation detectors, Geiger counters, or scintillation detectors. The main goal of radiation detection is to identify the presence and type of radiation in a given area or material.
Radiation monitoring, on the other hand, is a broader concept that encompasses the continuous measurement of radiation levels over time. Radiation monitoring involves the use of devices such as personal radiation dosimeters, area radiation monitors, or environmental radiation monitors to measure and track radiation levels in a given environment or over a specific time period. The primary goal of radiation monitoring is to ensure that radiation levels remain within safe limits and to provide early warning of any potential radiation hazards.
In summary, radiation detection is focused on identifying the presence and type of radiation, while radiation monitoring involves ongoing measurement and tracking of radiation levels over time to ensure safety and provide early warning of potential hazards.
When choosing a radiation monitoring device, there are several factors that should be considered:
Overall, it’s important to consider the specific requirements of the application when choosing a radiation monitoring device to ensure that it can accurately measure the type and range of radiation needed, while also being practical for the environment in which it will be used.
The accuracy of radiation monitors in measuring radiation levels depends on several factors, including the type of radiation being measured, the sensitivity of the device, and the calibration of the device. In general, modern radiation monitoring devices are highly accurate and can provide precise measurements of radiation levels.
Most radiation monitors are calibrated to measure radiation levels in units of Sieverts (Sv) or microSieverts (μSv) per hour. These devices typically have a margin of error of less than 10%, which is considered highly accurate for most applications.
However, it’s important to note that radiation monitoring devices can be affected by a variety of factors that can impact their accuracy. For example, certain types of radiation can be more difficult to detect than others, and some types of radiation can cause interference with other types of monitoring equipment.
Additionally, external factors such as temperature, humidity, and other environmental conditions can also affect the accuracy of radiation monitoring devices. To ensure the accuracy of radiation monitoring equipment, it’s important to regularly calibrate and maintain the devices and to follow proper procedures for their use and interpretation of their readings.
There are many different types of radiation monitoring devices, but some common features include:
Radiation can be measured in several ways, including:
Different types of radiation require different measurement techniques, and different measurement techniques may be more appropriate depending on the application.
Regular calibration of radiation monitoring devices is extremely important to ensure accurate measurements of radiation levels. Over time, factors such as wear and tear, temperature changes, and exposure to radiation can cause the sensitivity of the detector to change, leading to inaccurate readings. Calibrating a radiation monitoring device involves exposing it to a known amount of radiation and comparing the reading on the device to the expected value. If there is a discrepancy between the measured value and the expected value, adjustments can be made to correct the calibration of the device.
By regularly calibrating radiation monitoring devices, you can ensure that the device is measuring radiation levels accurately and reliably. This is particularly important in environments where people are exposed to ionizing radiation, such as nuclear power plants or medical facilities. Accurate measurements can help to minimize the risk of radiation exposure and ensure the safety of workers and the general public.
Modern radiation monitoring devices incorporate a range of advanced technologies to improve their accuracy, sensitivity, and functionality. Some of the most advanced technologies used in modern radiation monitoring devices include:
By incorporating these advanced technologies, modern radiation monitoring devices are able to provide more accurate and reliable measurements of radiation levels, helping to ensure the safety of workers and the public in radiation-prone environments.
To choose the right radiation monitoring device for your workplace, you should consider factors such as the type and level of radiation present, the frequency of monitoring, and the specific needs of your industry or application. It is also important to select a device that meets regulatory requirements and has the necessary features for accurate measurement and analysis.
Inteccon offers a wide range of radiation monitoring devices that are reliable, accurate, and tailored to meet the needs of various industries and applications.
S.E. International, Inc. is a company that specializes in developing and manufacturing radiation detection instruments under the brand name Radiation Alert®. Since 1979, they have been dedicated to providing cost-effective and reliable instruments for personal and industrial use. Their diverse product line includes handheld instruments, area monitors, multichannel analyzers, and portable laboratories. The company is committed to community involvement and supports local projects and non-profits. Their team has received recognition for their international sales efforts and unparalleled support. Free software and updates are included with the purchase of any Radiation Alert® instrument. S.E. International, Inc. can be found at industry trade shows and in various industry magazines.
The Monitor 4 is a compact, analog radiation detector capable of detecting alpha, beta, gamma, and x-rays over 3 selectable ranges. With a proven and reliable design, it is simple and ergonomic, featuring a red count light and beep for each detected count, as well as battery check and silent operation. The Monitor 4EC offers the same features, with the added benefit of energy compensation for a linear response to gamma and x-rays above 40 keV.
The MC1K is a handheld survey meter that uses a built-in energy-compensated GM detector to detect gamma and x-rays up to 1000 mR/hr over 4 selectable ranges. It has a linear response to gammas and x-rays and a beep sound and count light flashes with each event detected.
The Ranger is a small, handheld survey meter designed for industrial environments but also suitable for laboratory use. It can detect low levels of alpha, beta, gamma, and x-rays and has built-in efficiencies for common isotopes to calculate activity in Bq and DPM. The instrument has a backlit digital display, red count light, and beeper that sounds with each count detected. Other features include selectable alert levels, an adjustable timer, and an optional wipe test plate for swipes. The Ranger has internal memory and comes with free Observer USB Software for downloading data, setting computer alarms, and calibrating the instrument. The detector is an internal halogen-quenched, uncompensated GM tube with a thin mica window and an effective diameter of 45 mm. The Ranger operates in a range of mR/hr .001 – 100, CPM 1 – 350,000, µSv/hr .01 – 1000, and CPS 0 – 5000. It runs on two AA alkaline batteries and comes with a carrying case, Xtreme Boot, Lanyard, Stand, Mini-USB Cable, Observer USB Software Download, and Certificate of Conformance. The Ranger has a 1-year limited warranty and also has anti-saturation capabilities.
The Ranger EXP is a compact and lightweight survey meter designed for use in tough environments. It has a sensitive detector that can detect low levels of alpha, beta, gamma, and x-rays, and a digital display with a red count light and audio indicator. The meter has an adjustable timer, selectable alert, and anti-saturation feature, and can be calibrated using the free Observer USB Software Family. It operates on two AA alkaline batteries and comes with a carrying case, Xtreme Boot, Lanyard, Stand, Mini-USB Cable, and Certificate of Conformance. Optional NIST calibration is available and the meter comes with a 1-year limited warranty.
This is a digital monitor for measuring ionizing radiation, capable of detecting beta, gamma, alpha and X-ray energy with low sensitivity. It features a GM halogen tube for measurement, a retro digital LCD screen, configurable alarm, and an internal beeper with an output range of 70 dB to 1 meter. The device has an operating range of 0.01-2000 μS / hr with units mR / hr, CPM and CPS and has an accuracy of +/- 15% of the reading. It can be operated through 2 AA alkaline batteries and has a USB output for use with Observer software. The compact size and high performance of this device make it an ideal tool for general radiation measurements.
The Radiation Frisker is a lightweight, handheld radiation contamination instrument that detects alpha, beta, and gamma. It has a backlit digital LCD display with customizable alarm levels and a radiation event count light. The device uses a GM halogen tube with a thin mica window and has an operating range of 1-500000 Ns/Hr with units µRHr, CPM and CPS. The Radiation Frisker has a sensor integrated into the instrument and an internal alarm beeper from 70 DB to 1 meter. It runs on 2 AA alkaline batteries and has an operation time of up to 2000 hours.
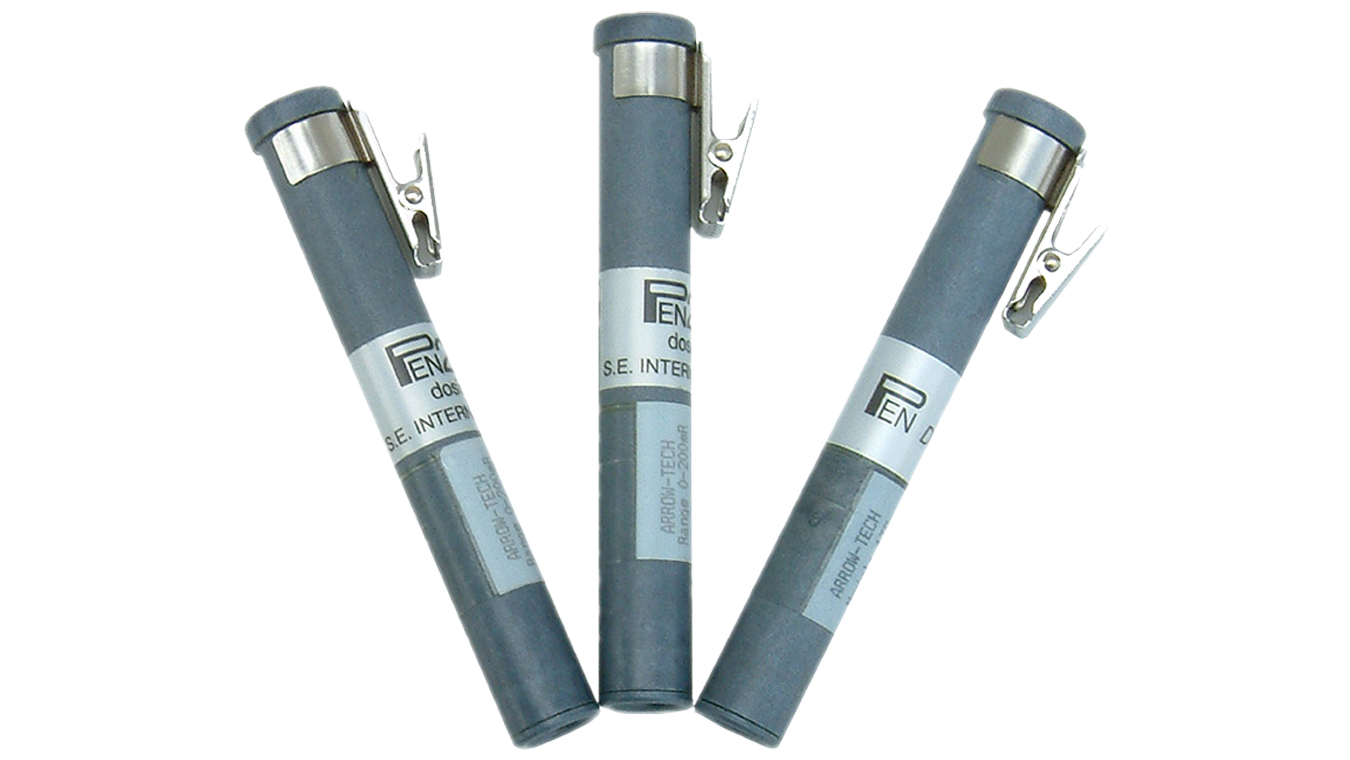
The advanced PENs are direct reading radiation dosimeters that measure and directly read accumulated dose of gamma and x-ray exposure. They are rugged, precision instruments with a higher quality and reliability than other dosimeters of its type. The dosimeter has a sturdy metal clip to attach it to a pocket or any object for monitoring total radiation exposure. It is hermetically sealed and immersion proof, designed to satisfy military specifications for the RADIAC METER IM-264/PD and ANSI N 13.5 and N322 requirements. It has an accuracy of +/-10% actual dose for Cs-137 or Co-60 and is resistant to power dependency of 16 Kev to 6 Mev. An optional dosimeter charger is available for the instrument waxy.
The Radiation Alert® Sentry EC is a compact personal dosimeter and rate meter designed to ensure the safety of personnel in occupations with potential gamma or x-ray exposure. It has an energy-compensated GM tube for a linear response to gamma and built-in memory for recording data points for tracking accumulated exposure. The unit has a range of 0.1-1 µSvHr for dose and 0.1-1 µSv for cumulative dose, with audible and vibration alarms that can be set using the SentryCom software. It also features an accuracy of +/-15% actual dose for Cs-137, a USB connection for PC and software, and operates via a 9V alkaline battery for 1500 hours of operation.
The RAD-60 is a digital personal dosimeter designed for everyday radiation monitoring. It features a silicon diode detector, a digital display, and an audible alarm with adjustable levels. The dosimeter has a 5-dose operation range from 1 µSv/Hr to 3 Sv/Hr and a cumulative dose operating range from 1 µSv to 9.99 Sv. It also has internal memory data logging and an infrared port for connection to a computer. The dosimeter is powered by a single AAA alkaline battery, which provides up to 1800 hours of operation.
The Radiation Alert Ranger is a handheld, digital radiation detector that offers excellent sensitivity to low levels of alpha, beta, gamma, and x-rays. It has built-in efficiencies for common isotopes and can calculate activity in Bq and DPM. The device has a backlit digital display, red count light, and a beeper that sounds with each count detected. It also has selectable alert levels, an adjustable timer, and an optional wipe test plate for swipes. The Ranger has internal memory and free Observer USB software for data download and computer alarms. It can be used in industrial environments and has a high-brightness strobe alarm and integrated horn with remote mounting capability. The device has an Ethernet connection, 3 relays, and a USB port for data logging and remote configuration. It runs on 12 VDC current and has a battery backup for up to 7 hours.
Tel +1 561-912-9809 / 561-9112-7201
E-mail [email protected]
6590 W Rogers Circle Suite# 11&12
Boca Raton – FL 33487
+1 561-912-9809 / +1 561-912-7201
[email protected]
6590 W Rogers Circle, Suite #11&12
Boca Raton, FL 33487