
Sound and vibration are two important aspects of the environment that can greatly impact our health and well-being. In many industrial and work settings, exposure to high levels of noise and vibration can cause a range of physical and mental health problems. This is why it’s crucial to understand the nature of sound and vibration, as well as the measures that can be taken to reduce the harmful effects of exposure.

Sound is a type of energy that travels through the air and is characterized by fluctuations in air pressure. When these fluctuations reach our ears, we perceive them as sound. Sound is an essential part of our daily lives, providing us with information, entertainment, and a sense of the environment around us. However, it is important to note that when sound is too loud or prolonged, it can become dangerous to our health, leading to hearing damage and other related issues.
Sound waves are a series of pressure waves that travel through a medium, such as air or water. These waves are created when an object vibrates, causing the surrounding air molecules to move. This movement creates pressure variations that propagate away from the source of the vibration, forming a sound wave. Sound waves are an important aspect of our environment, providing us with information about the world around us.
Examples of sound waves can be found in a variety of settings, including factories, constructions, mines, and other industrial sites. These sound waves can come from a range of sources, including machinery, power tools, and other equipment.
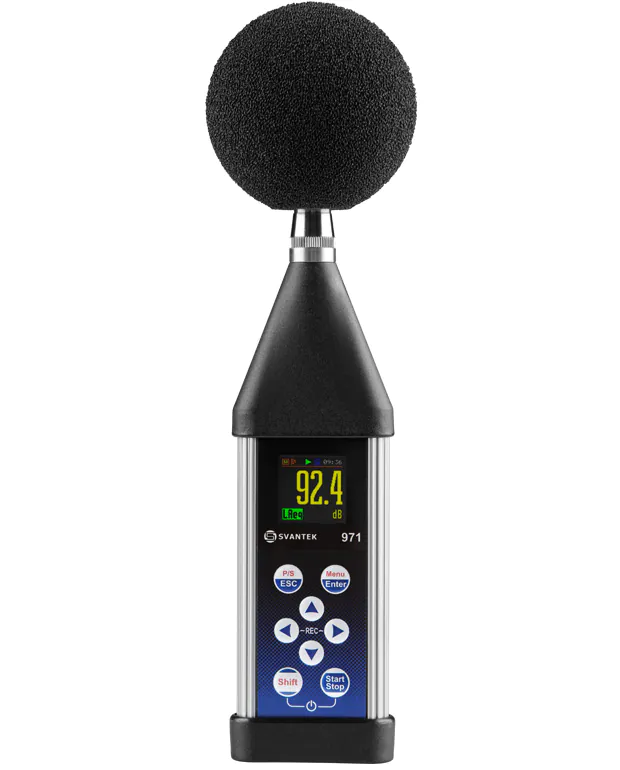
Sound is measured using specialized instruments such as sound level meters and noise dosimeters. A sound level meter is a device equipped with a microphone that detects air pressure changes and converts them into an electrical signal. This signal is then converted into a digital form, allowing the measurement to be displayed on a screen or recorded in the device’s memory.
Noise dosimeters are similar to sound level meters, but they are designed to be worn near the ear to measure personal noise exposure. These devices are often used in occupational settings to prevent noise-induced hearing loss.
Decibels (dB) are a unit of measurement used to quantify the volume of sound. Decibels measure the sound pressure level (SPL) of a sound wave and provide a standardized way to compare the loudness of different sounds. For example, a sound with an SPL of 60 dB is considered to be 10 times louder than a sound with an SPL of 50 dB.
Exposure to high decibel levels can cause hearing damage, especially if the exposure is prolonged. The Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) recommends a maximum exposure limit of 85 dB over an eight-hour period. This limit is based on the assumption that exposure to higher levels of noise can cause permanent hearing damage.
Examples of situations where exposure to high decibel levels can occur include manufacturing facilities, construction sites, airport operations, and other industrial settings. In these environments, workers may be exposed to high levels of noise from machinery, power tools, and other equipment.
It is important for employers to monitor and control noise levels in the workplace to ensure the safety and well-being of their employees. OSHA has established guidelines for controlling noise exposure in the workplace through the Occupational Noise Exposure standard (29 CFR 1910.95). This standard outlines the requirements for employers to implement engineering and administrative controls to reduce employee exposure to hazardous noise levels.
The standard also requires employers to provide hearing protection and annual hearing tests to workers who are exposed to noise levels above 85 dB over an eight-hour period. Employers must also provide training to employees on the hazards of noise exposure and the importance of using hearing protection. The OSHA standard can be found on the OSHA website and provides detailed information on the requirements for controlling noise exposure in the workplace.
Prolonged exposure to high levels of noise can cause a range of health problems, including hearing damage, stress, and other illnesses. One of the most common effects of noise exposure is the loss of hearing, which can occur gradually over time or as a result of a single, loud event. In addition to hearing damage, noise exposure can also cause stress, anxiety, and other mental health problems.
Studies have shown that exposure to high levels of noise can increase the levels of stress hormones in the body, leading to feelings of anxiety and stress. This can lead to a range of health problems, including high blood pressure, heart disease, and sleep disturbances. In addition, noise exposure has been linked to a number of cognitive problems, such as decreased productivity, reduced attention span, and decreased ability to process information.
The effects of noise exposure can be even more pronounced in children, who are still developing their auditory system. Children who are exposed to high levels of noise for extended periods of time may experience hearing damage, difficulty concentrating, and behavioral problems. In order to minimize the risks associated with noise exposure, it is important for individuals to protect their hearing by wearing appropriate hearing protection and limiting their exposure to loud noises.
It is also important for employers to take steps to minimize the risk of noise exposure in the workplace. This can include implementing engineering controls, such as enclosing loud machinery, and providing workers with hearing protection. In addition, employers should provide their workers with regular hearing tests to monitor for any signs of hearing damage and to ensure that they are taking appropriate steps to protect their hearing.
Vibration refers to the rapid movement back and forth of an object or a material. Vibrations can occur in many forms, including mechanical, acoustic, and seismic vibrations. Vibrations are often caused by machinery, vehicles, or other sources of intense energy. They can also be caused by natural events such as earthquakes, volcanic eruptions, or wind.
In the workplace, vibration exposure is a common issue, especially for workers who operate heavy machinery, handheld power tools, or other equipment that generates intense vibrations. Prolonged exposure to vibration can lead to a number of physical health problems, including hand-arm vibration syndrome (HAVS), back pain, neck pain, and circulatory problems.
Vibrations are measured using specialized instruments known as vibration monitors that are calibrated with vibration calibrators. These instruments are equipped with sensors that detect the vibrations and convert them into an electrical signal. The electrical signal is then processed and displayed on a display or recorded in the monitor’s memory.
Vibration monitors are an essential tool for workers who are exposed to vibration in their jobs. They allow workers to monitor their exposure levels and assess their potential risk of developing physical health problems. By using vibration monitors, workers can take steps to reduce their exposure levels and protect their health.
There are two main types of vibrations that workers are exposed to in the workplace: hand arm vibration and whole-body vibrations. Human vibrations are generated by the use of handheld power tools, heavy machinery, and other equipment that produces intense vibrations. These vibrations can be transmitted to the body, leading to a range of physical health problems.
Building vibrations are generated by external sources, such as nearby construction sites, airports, or other sources of intense energy. Building vibrations can affect the structural integrity of a building and cause discomfort to the workers inside. Whole-body vibrations, on the other hand, are motions transmitted to the human body as a whole through the supporting surfaces, such as the feet of a standing person or the supporting area of a seated person. This type of vibration is found in vehicles, machinery, and in the vicinity of working machinery. Hand arm vibration is caused mainly by the use of handheld power tools or machinery such as grinders, disc sanders, random orbital sanders, etc.
Prolonged exposure to vibration can lead to a number of physical health problems, including hand-arm vibration syndrome (HAVS), back pain, neck pain, and circulatory problems. HAVS is a common condition among workers who use handheld power tools on a regular basis. Symptoms of HAVS include numbness and tingling in the fingers, decreased grip strength, and changes in skin temperature.
Back pain and neck pain are also common problems among workers who are exposed to vibration in their jobs. These conditions can be caused by the repeated shocks and stress that the body is subjected to when exposed to vibration.
Circulatory problems are another potential consequence of prolonged exposure to vibration. These problems can be caused by the reduction of blood flow to the extremities, leading to cold fingers and toes, and an increased risk of injury. The most common is Raynaud´s syndrome
Tel +1 561-912-9809 / 561-9112-7201
E-mail [email protected]
6590 W Rogers Circle Suite# 11&12
Boca Raton – FL 33487
+1 561-912-9809 / +1 561-912-7201
[email protected]
6590 W Rogers Circle, Suite #11&12
Boca Raton, FL 33487