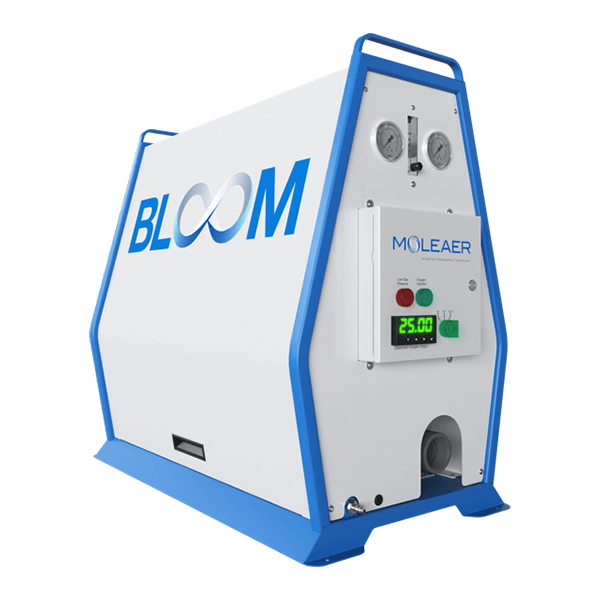

Water is an essential resource for all living things and human activities. However, the quality of water has become a major concern due to the impact of human activities on the environment. Various government agencies and environmental institutions have made it a priority to measure water quality and control pollution levels. To achieve this, water quality monitors are used to monitor different types of water bodies and assess their current condition in terms of parameters such as pH, OD, conductivity, turbidity and others. As a health and safety professional, it is important to ensure that these monitors are used correctly to minimize risks to human health and the environment. Therefore, it is important to understand the importance of water quality monitoring and its role in maintaining a healthy environment for all.

Monitoring water quality involves regularly testing and analyzing various parameters to determine the presence and concentration of pollutants or contaminants in the water. Here are some of the steps involved in monitoring water quality:
Water quality can be monitored by a variety of individuals and organizations, depending on the source and intended use of the water. Here are some examples:
Overall, water quality monitoring is a shared responsibility that involves a number of stakeholders working together to protect public health and the environment.
A water quality monitor and a regular water monitor are two different types of devices used to measure different aspects of water.
A water quality monitor is a device that is used to measure various physical, chemical, and biological characteristics of water, such as pH, temperature, dissolved oxygen, turbidity, and nutrient levels. It is used to assess the overall quality of water for a specific use, such as drinking water, recreational water, or aquatic life support.
On the other hand, a regular water monitor is a device used to measure the quantity or flow rate of water. It is used to determine the volume of water flowing through a pipe or other water system at any given time. This type of device is commonly used in water distribution systems to monitor and control the flow of water.
In summary, a water quality monitor measures various characteristics of water to assess its quality, while a regular water monitor measures the quantity or flow rate of water in a system.
Tel +1 561-912-9809 / 561-9112-7201
E-mail [email protected]
6590 W Rogers Circle Suite# 11&12
Boca Raton – FL 33487
+1 561-912-9809 / +1 561-912-7201
[email protected]
6590 W Rogers Circle, Suite #11&12
Boca Raton, FL 33487